Luna
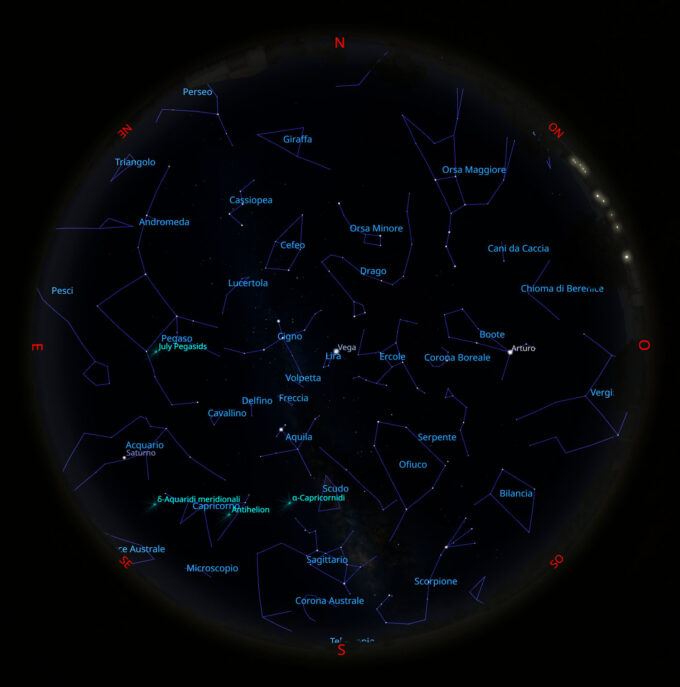
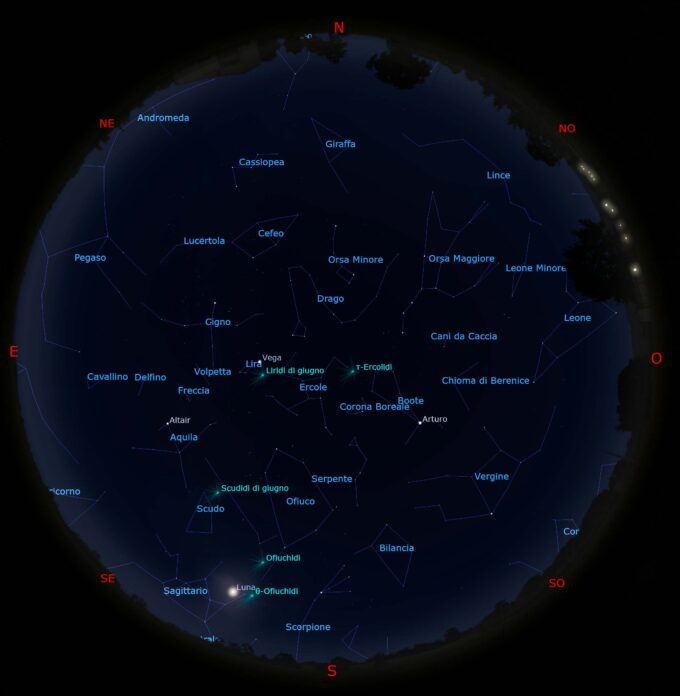
Il cielo di luglio 2023
Il Sole Le informazioni sono tratte dal Cielo del mese di luglio 2023 a cura della UAI. Attualmente il Sole si trova nella...
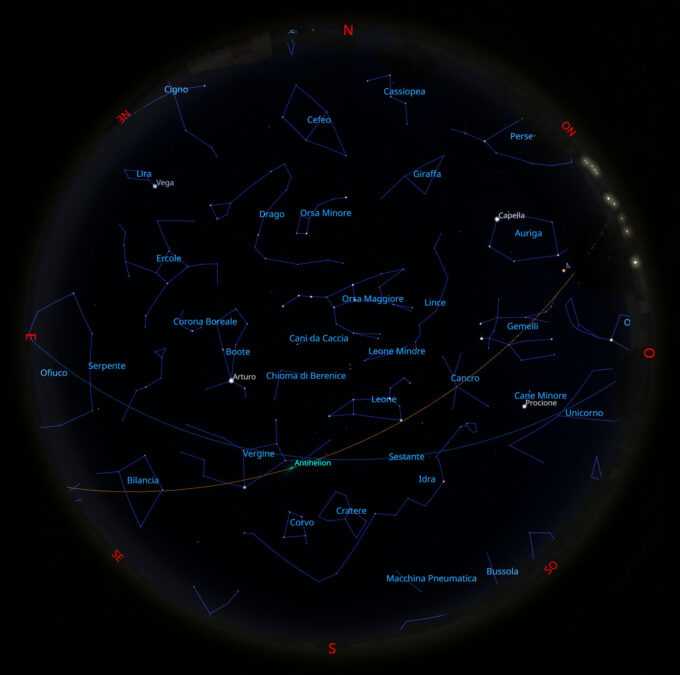
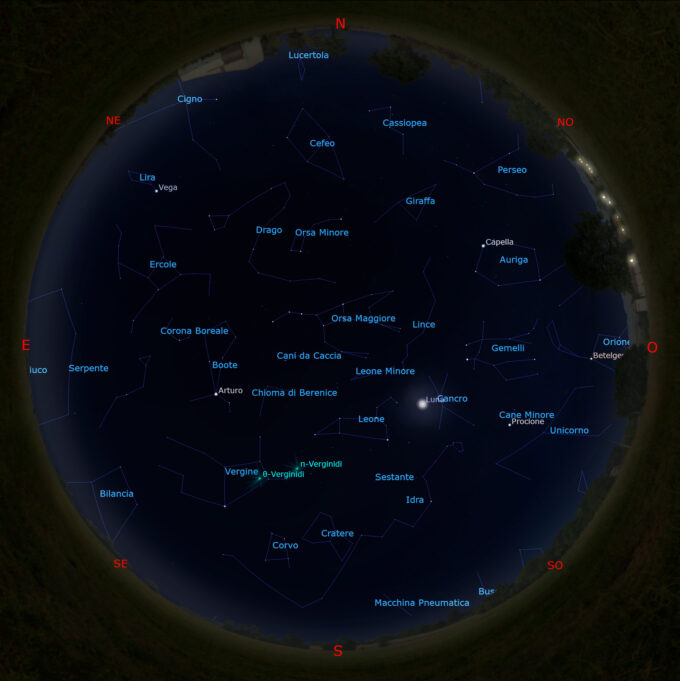
Il cielo di marzo 2023
Il Sole Attualmente il Sole si trova nella costellazione dell’Acquario e il giorno 12 marzo si muoverà nella costellazione dei Pesci. Il 20...
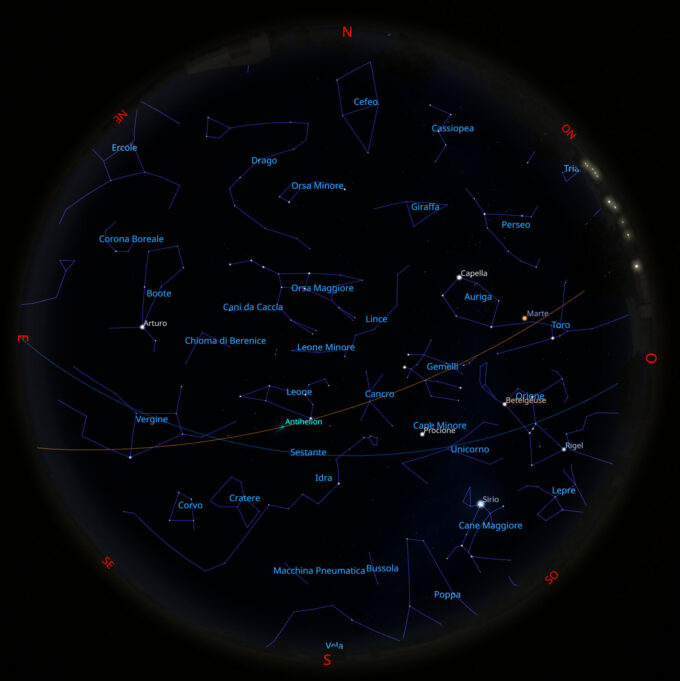
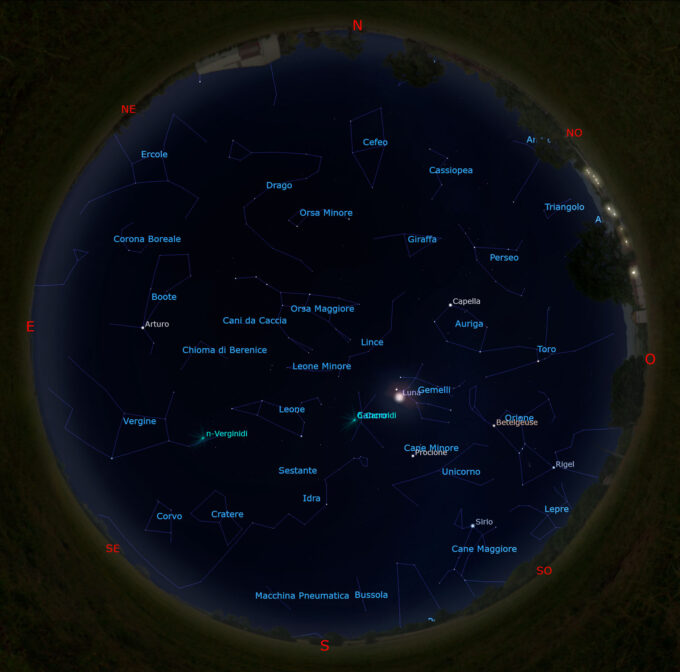
Il cielo di febbraio 2023
Per chi desiderasse avvicinarsi all’osservazione del cielo stellato a occhio nudo o al telescopio, è disponibile il mio primo libro intitolato “Il cielo...
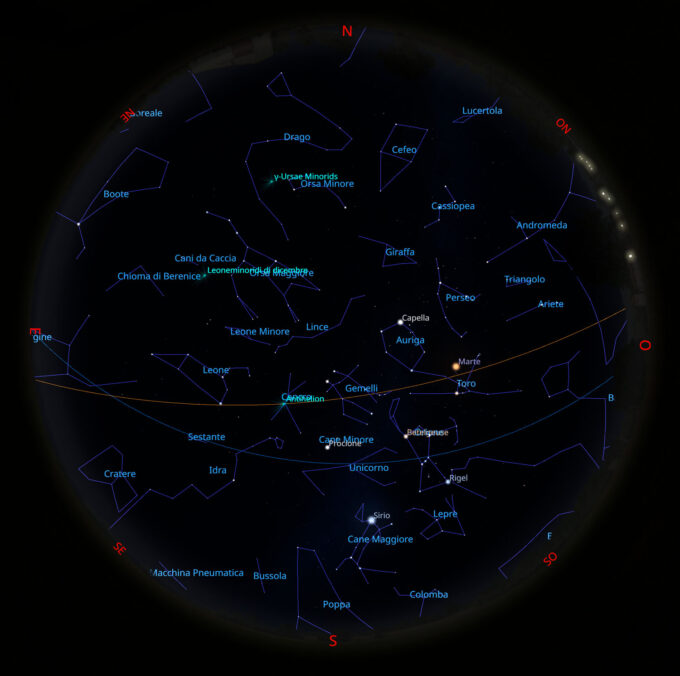
Il cielo di gennaio 2023
Per chi desiderasse avvicinarsi all’osservazione del cielo stellato a occhio nudo o al telescopio, è disponibile il mio primo libro intitolato “Il cielo...
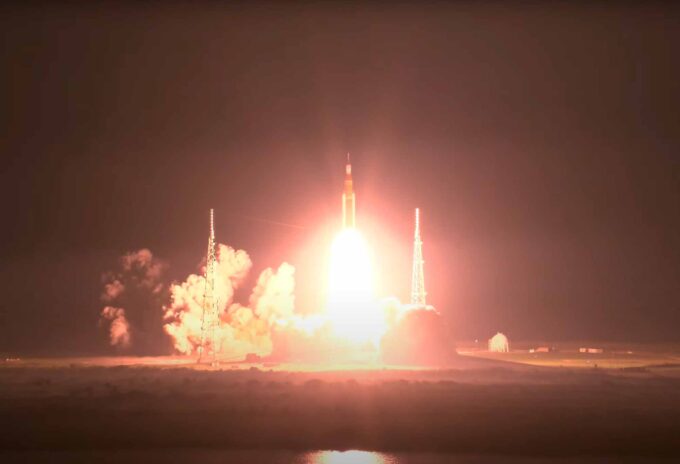
La missione Artems 1 in viaggio verso la Luna
Dopo diversi rinvii dovuti a problemi tecnici, perfettamente normali per un razzo di nuovissima concezione, la missione Artemis 1 è in viaggio verso...
Il cielo di giugno 2022
Il Sole Le informazioni sono tratte dal Cielo del mese di giugno 2022 a cura della UAI. Attualmente il Sole si trova nella...
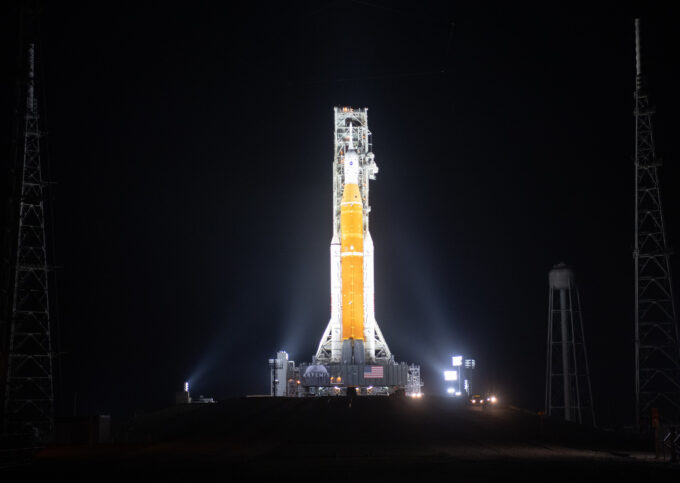
Lo Space Launch System pronto per il test finale
Chi è vissuto negli anni Sessanta rivedrà un’immagine familiare, ma pur sempre straordinaria. Chi è un po’ più giovane, come me, ha avuto...
Il cielo di marzo 2022
Il Sole Attualmente il Sole si trova nella costellazione dell’Acquario e il giorno 12 marzo si muoverà nella costellazione dei Pesci. Il 20...
Il cielo di febbraio 2022
Per chi desiderasse avvicinarsi all’osservazione del cielo stellato a occhio nudo o al telescopio, è disponibile il mio primo libro intitolato “Il cielo...